The Government reform in the health sector was to come up with a model that would best suit the user of the health service delivery. Health workers, public servants and users of the health systems have long suggested that laws governing the delivery of public and curative health services in the provinces create a fragmented system where public services are provided by the province under one law and curative services provided by public hospitals under a different law. As a result, there are different administrative arrangements and financing arrangements. Coordination and cooperation is difficult. This affects the outcomes of the system and the people who use it.
PHA Act 2007
In 2007, a new law was drafted and, after consultation with stakeholders, on May 1, 2007 The National Parliament of Papua New Guinea unanimously passed the Provincial Health Authority Act.
The purpose of the new law is to enable provinces to choose an alternative model for the delivery of Government funded health service so that the systems works better for the people run it and the people who use it. Provinces were given options to choose to create a provincial health authority to deliver both public health services and curative health under one system tasol.
Partnership Agreement
Eastern Highlands Province was the first in the country under the former Governor late Malcolm Kela Simith to have agreed to establish a new health reform the Provincial Health Authority in the Province. The partnership agreement was signed on 22nd June 2009 at the University of Goroka (UOG) between the National Minister of Health, Honorable Sasa Zibe and Late Hon. Malcolm Kela Smith Former Governor EH Provincial Government. This agreement signified the release of all staff, facilities, equipment’s and other assets from both the National department of health for Goroka General Hospital and the Rural Health Services from the EH Provincial Government to the EH Provincial Health Authority.
Ministerial Order
The Eastern Highlands Provincial Health Authority (EHPHA) was officially established under a Ministerial order issued on the 12th June 2012. This is a single system of management of health service delivery in the province in which the Executive Management reporting to the Board and the Board to the National Minister for Health. (one system tasol).
- Single Governance board.
- Single Executive Management.
- Single Financial Management.
- Single Human resource & payroll system
- Single reporting
- Single monitoring & evaluation
Health Service Management
Provincial Profile
Eastern Highlands Province is situated in the highlands of PNG and shares a common administrative boundary with Madang, Morobe, Gulf and Simbu provinces. It has an area mass of about 11, 200 square kilometres. The province has eight (8) administrative districts and 24 local Level Governments (LLGs). The projected population of the province in 2020 from 2011 census is about 717,957 with an annual growth rate of 3%. The province depends mostly on agricultural sector, particularly coffee as its cash crop and recent economy of the province is increasing with major developments taking place.
Map of Eastern Highlands Province
Eastern Highlands is known for its rugged mountain terrains and broad valleys and most of the rural population is reachable by road and air transports. Unfortunately, these roads and airstrips serving the rural population are in debilitating state and making difficult for our sector to reach the rural populations. The health services provided in the province are through government, churches and various organizations including institutional clinics and private practitioners.
The Districts
Eastern Highlands Province comprises of eight (8) Administrative Districts and is headed by a District Administrator and as Chief Executive officer to the District Development Authority.
The office of the District Administrator (DA) is supported by various Divisional Heads of Government Services in the districts including Health being headed by a District Health Officer (DHO) or administratively known as the Principal Project Officer Health (PPO) in each of the districts.
We have the 8 districts namely; Daulo, Goroka Urban, Ungai-Bena, Lufa, Henganofi, Okapa, Kainantu and Obura-Wonenara districts. In each, Eastern Highlands health facilities are established.
Eastern Highlands Province Population Distribution
According to the 2011 National Census, the population of Eastern Highlands Province was at 579,825 with a population Growth Rate of 3% per year. The provincial population in 2020 is projected to be 717,917.
Population Distribution by District
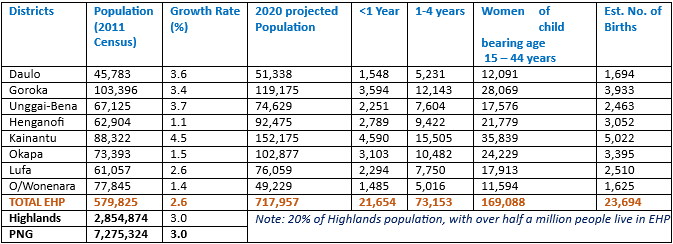
Distribution of Health Facilities in Eastern Highlands Province
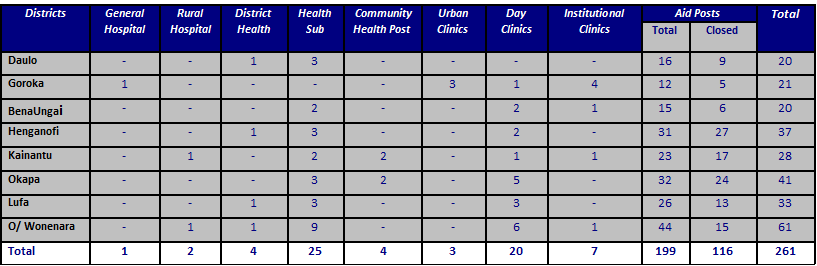
Health Services in the Province are delivered from a network of health facilities. These include Goroka General Hospital, Kainantu & Okapa Rural Hospitals, 4 District Health Centers, 25 Health Centers, 3 Urban Clinics, 20 Day Clinics and 163 Aid Posts.
A little over 40% of these facilities are managed by the Christian Health Services and other 3% are owned and operate by private practitioners and Institutions as closed clinics.
Health Facilities in Eastern Highlands Province operating under Eastern Highlands Provincial Health Authority
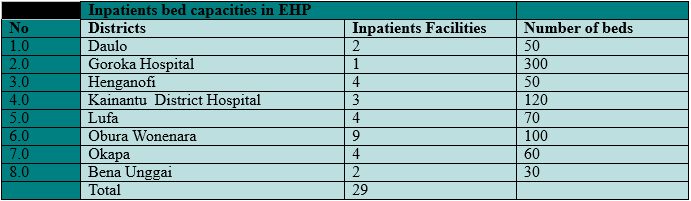
Bed capacity in Health Facilities.
Hospitals and the Health Centers and some Day Clinics provide inpatients cares to the communities.
The Total Bed Capacities is 780 in the province from which 62% (n = 480) are at the Rural Health Services while the other 38% (n = 300) are at Goroka General Hospital.
Distribution of Bed capacities in Eastern Highlands Provincial Health Authority health facilities by Districts.
Eastern Highlands Provincial Health Authority Board and Governance
Purpose of the Eastern Highlands Provincial Health Authority Board
The Provincial Health Authority board is the Governance board and has powers to be responsible for all health matters within the province and is responsible to perform the following duties;
- Enter into contracts.
- Consultation with the Department of health.
- Recommend for fees and charges payable for the provision of health services.
- Raise funds and resources.
- Make grants to health service providers and accept gifts from donors and partners.
Boards Term of Office
The board as per the PHA Act has a term of office for three (3) years. The active period is from the date of the gazettal to the next expiry date in the third (3) year.
Eastern Highlands Provincial Health Authority Governance Structure
This is the overall organizational structure through which supervisory roles are performed, communications are channeled through and submission of reports on service delivery being submitted. It reflects the channel of command and the levels of authority of the organization. It also shows the reporting structure and the relationships of EHPHA with the District Development Authorities, Provincial Government and the National Government.
Eastern Highlands Provincial Health Authority Governance and Reporting Structure.
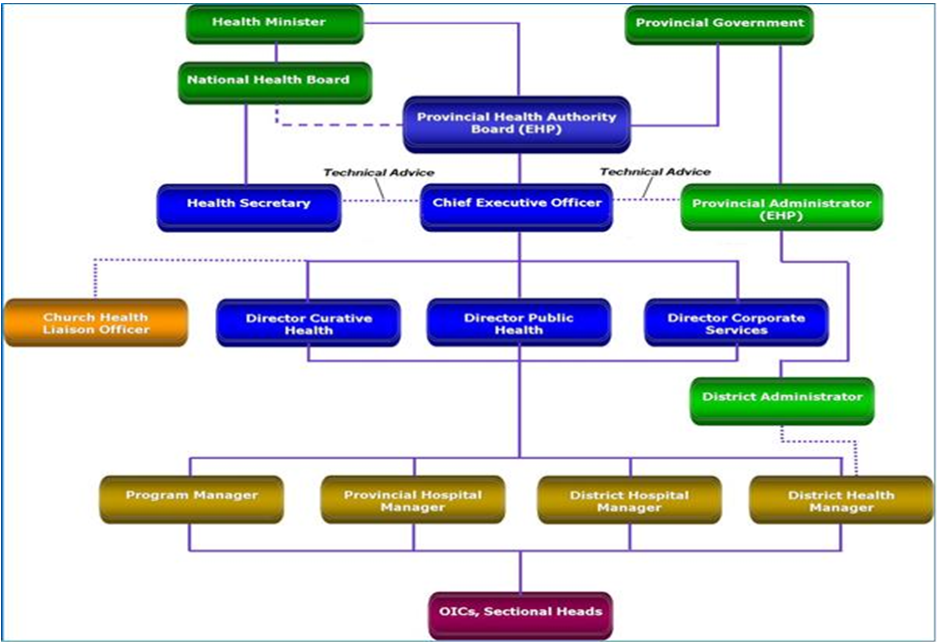
The Executive Management
Members of the Executive management represent the Chief Executive officer, the Director curative Health, Director Public Health and Director Corporate Services. The senior executive management team are responsible for the implementation of the respective directorate’s activities and the management and board resolutions and directives and provide the directorate reports as required to the office of CEO.
Senior Executive Management Team

Eastern Highlands Provincial Health Authority (EHPHA) was established under the PHA Act 2007, with a single governance board and the executive management team to maintain good governance and accountability in carrying out its purpose and responsibilities in delivering health care services in Eastern Highlands Province.
The health service structure for EHPHA has a Governing Board to oversee and govern the organization, while the Chief Executive Officer serves as the deemed departmental head and the chief accountable officer. Meanwhile, the three directorates govern and manage the delivery of health services in the province under the single authority.
The Directorate of Curative Health is responsible for the management of the Provincial Hospital, District Hospitals, clinical governance and curative component of health services in the province.
The Directorate of Public Health is responsible for districts health services, technical health programs and mostly preventative health services.
The Directorate of Corporate Services provide support service (administrative services) in terms of finance management, Policy & Planning, ICT, HR functions and logistics, Fleets and facility management to clinical directorates to operate efficiently and effectively in the delivery of health services in the province.
The Senior Executive Management
The senior Executive Management is the highest management team in the organization that makes decision for the
implementation of the delivery of the health services in the province and advices the PHA Board through the office of the CEO.
Performance of the Senior Executive Management
- Attend quarterly EH PHA board meeting.
- Conducted Senior Executive Management team meeting on a monthly bases.
- Conduct EH PHA disciplinary committee meeting.
- Provincial staff development and training committee meeting.
- Conducted provincial project steering committee meeting.
- Appointed as deputy controller for the covid-19 outbreak in the province.
- Deputy Chairman of the covid-19 provincial coordinating committee in the province.
- Accepting and signing of the partnership agreements with the development partners, NGO’S and Faith based organizations to assist with the delivery of health service in the province.
- Conducted the 2020 health services performance review of the province.
Eastern Highlands Provincial Health Authority Management Structure

Executive Services
The executive services, is the office of the chief executive officer that is responsible to the EH PHA governance board
and the deemed departmental head responsible for all the public servants matters and the chief accountable officer managing and controlling the health services funding for the development projects, salaries and allowance for the health workers and the operational funding to the organization including, funds raised internally as revenue and funds from development partners for intervention program and projects.














































